Toshio IBE*, Yuichi MATSUMURA†, Toshihide UENO†, Hajime KIYOKAWA†, Susumu YONEZAWA†† and Masayuki TAKASHIMA††
Fukui Prefectural Industrial Technology Center; 61-10 Kawaiwashizuka, Fukui-shi 910-0102 Japan † Kiyokawa Plating Industry Co., Ltd.; 1-414 Wadanaka, Fukui-shi 918-8515 Japan †† Faculty of Engineering, Fukui University; 3-9-1 Bunkyo, Fukui-shi 910-8507 Japan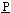 oly
oly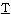 etra
etra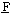 luoro
luoro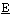 thylene) composite film was formed on hydrogen storage alloy (MH alloy) powder particles by means of electroplating method. MH alloy powder (mean diameter, 50 μm)with the composition of MmNi3.65Co0.75Al0.25Mn0.35 (Mm denotes
thylene) composite film was formed on hydrogen storage alloy (MH alloy) powder particles by means of electroplating method. MH alloy powder (mean diameter, 50 μm)with the composition of MmNi3.65Co0.75Al0.25Mn0.35 (Mm denotes 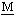 isch
isch 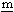 etal)was used. The electroplating apparatus equipped with rotating bath was designed to electroplate the Ni-PTFE composite film on the MH alloy powder particles. The bath was rotated at high speed (350 rpm) to make electrical contact between the particles and the belt-ring cathode made of titanium placed on the inside wall of the bath. The electrolyte solution added MH alloy powder and PTFE powder was agitated by intermittent rotation. PTFE powder particle (mean diameter, 5 μm) was suspended in the electrolyte solution with a cationic surfactant.
etal)was used. The electroplating apparatus equipped with rotating bath was designed to electroplate the Ni-PTFE composite film on the MH alloy powder particles. The bath was rotated at high speed (350 rpm) to make electrical contact between the particles and the belt-ring cathode made of titanium placed on the inside wall of the bath. The electrolyte solution added MH alloy powder and PTFE powder was agitated by intermittent rotation. PTFE powder particle (mean diameter, 5 μm) was suspended in the electrolyte solution with a cationic surfactant.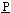 ressure
ressure 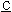 omposition
omposition  emperature) measurement, characteristics of hydrogen gas absorption-desorption such as the equilibrium pressure, the absorption amount and the hysteresis were found to be maintained. The corrosion resistivity in a strong alkaline solution was extremely enhanced. Even after immersing in 6 mol dm−3 KOH at 70 °C for 72 h, no formation of Mm (OH)3 on the surface of Ni-PTFE plated MH alloy was detected, and especially, the dissolving Mn decreased to less than one twentieth amount of original MH alloy.
emperature) measurement, characteristics of hydrogen gas absorption-desorption such as the equilibrium pressure, the absorption amount and the hysteresis were found to be maintained. The corrosion resistivity in a strong alkaline solution was extremely enhanced. Even after immersing in 6 mol dm−3 KOH at 70 °C for 72 h, no formation of Mm (OH)3 on the surface of Ni-PTFE plated MH alloy was detected, and especially, the dissolving Mn decreased to less than one twentieth amount of original MH alloy.